The economic cycles: how to understand it and benefit from it (part 1)
- George Solotarov
- Hits: 490
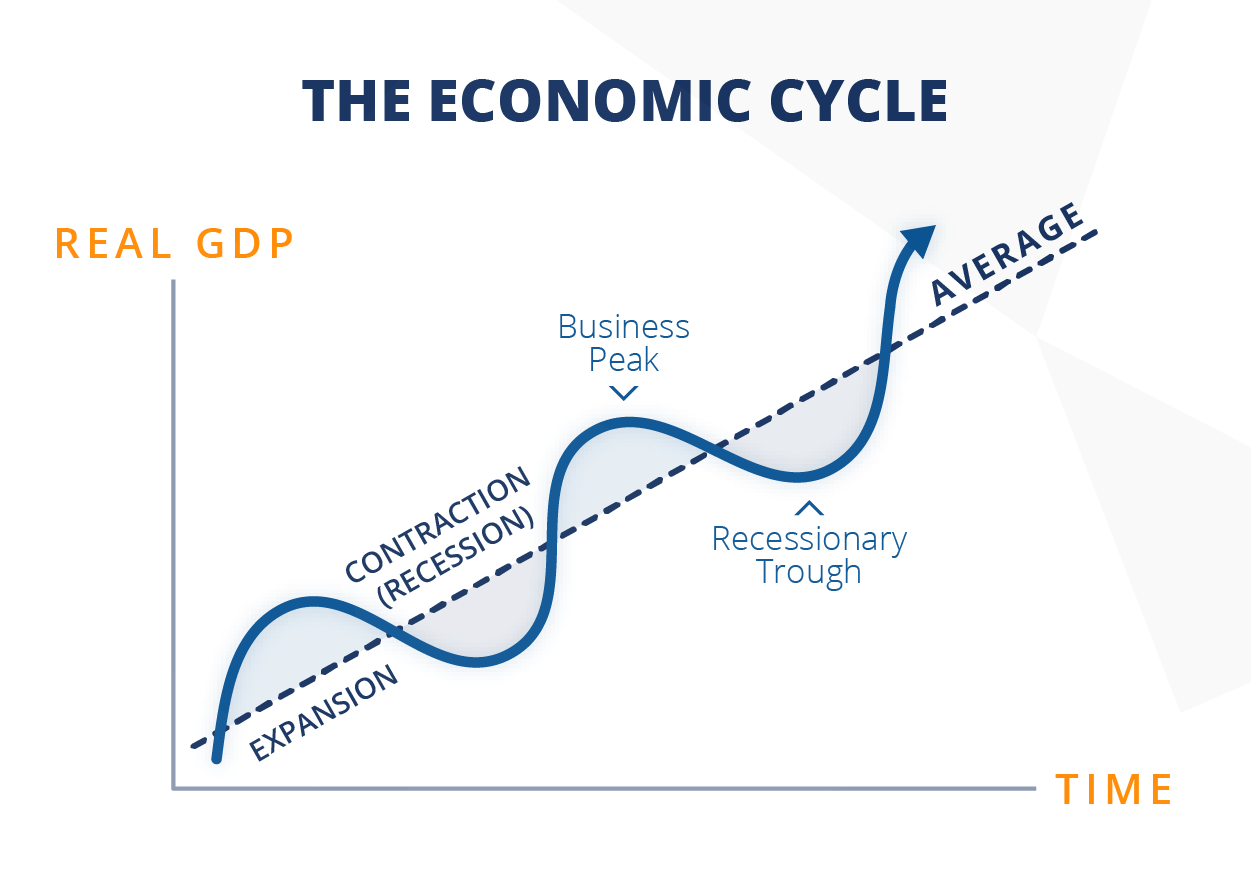
What are Economic Cycles
Economic cycles are periodic fluctuations in business activity ranging from boom to recession. It is important to understand that the economy remains in one of the phases of different economic cycles at any given time. The matter is complicated by the fact that these cycles always have different lengths of impact on the economy. At the same time, it is impossible to accurately predict the duration of each of them.
Any economic events are repeated at certain intervals, although at different levels. At the same time, the duration of the period from one economic peak to the next is rarely constant. In recent times, the most marked peaks coincided with the major wars of the 20th century, and the deepest and longest recession began after the First World War.
On the markets of some countries and even specific goods (oil, metal, grain, coffee, etc.) the economic situation is also constantly changing. Supply and demand are changing, and sales are falling or rising, which the market is able to adjust. Short-term changes in supply and demand can hide more complex, long-term processes, but they all usually end up being explained by the theory of economic (or business) cycles.
Why is the economy cyclical?
Because everything in nature is cyclical. Human history is also characterized by cycles; moreover, historians have been connecting economic cycles with political, cultural, etc. for a long time.
Going through each of the phases of the cycle, the economy develops, although of course, in a recession or depression, people are unlikely to agree with that. Sometimes it is possible to break the course of the economic cycle through political intervention in the natural course of economic processes (a revolution with a change of social order, a war), but this usually has very negative impacts.
Finally, the economic cycles should be considered as one of the tools of market self-regulation. This occurs under the influence of various causes that act on the economy both internally and externally. These include scientific breakthroughs, inventions of new ways of production, international economic interactions, unplanned increases/decreases in raw material and commodity stocks, raw material price dynamics, changes in regulations, spikes in consumer spending, and investment processes.
Stay tuned for our updates and in the next article, we will tell you about the different phases of the economic cycle and what the indicators of economic cycles are.
